
In an era where digital transformation is the backbone of every industry, cyberattacks have evolved faster than most organizations’ ability to defend themselves. From fintech companies securing millions of transactions per second, to government platforms protecting national data, the pressure to stay resilient against cyber threats has never been higher.
This is where Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing (VAPT) becomes a fundamental pillar of cybersecurity. VAPT doesn’t just identify weaknesses — it reveals how those weaknesses can be exploited in the real world, helping organizations strengthen their defense proactively.
In this article, we explore what VAPT is, its types, methodologies, frameworks, and why it is crucial for today’s digital ecosystem.
1. What Is Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT)?
VAPT (Vulnerability Assessment & Penetration Testing) is a structured process used to:
a. Identify security vulnerabilities in applications, networks, and systems
b. Validate the impact of those vulnerabilities through controlled exploitation
c. Recommend remediation steps to improve security posture
VAPT combines two primary components:
Vulnerability Assessment(VA)- A broad evaluation that identifies known security flaws using automated and manual techniques.
VA Goal: Breadth of coverage.
Penetration Testing(PT)- An ethical hacking exercise where testers try to exploit vulnerabilities the way an attacker would.
PT Goal: Depth of exploitation.
2. Internal vs External VAPT — Two Critical Approaches

External VAPT:
Simulates real-world attacks originating outside the organization. External VAPT assesses how easy it is for an outsider to compromise the organization. External VAPT Focus Areas:
a. VAPT of Public-facing Websites & APIs
b. VAPT Cloud assets
c. Perimeter firewalls
d. VAPT of External infrastructure
e. VAPT of Public facing Mobile Applications
f. VAPT of Public facing Thick Client Application
Internal VAPT:
Assumes the attacker already has a foothold inside the network (e.g., rogue employee, malware, phishing). Internal VAPT reveals how quickly an attacker could escalate privileges or move laterally once inside. Internal VAPT Focus Areas:
a. VAPT of Internal Network Devices, Servers, Firewalls etc
b. VAPT of Servers & workstations
c. Active Directory Penetration Testing
d. Network Segmentation
e. Wireless Device Penetration Testing
f. VAPT of Internal Websites, API and Mobile Applications
3. Why VAPT Is Important Across Industries?
🛡 For Organizations (Any Size):
a. Reduces attack surface
b. Prevents data breaches and downtime
c. Improves risk visibility
d. Protects brand reputation
f. Ensures compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC2, GDPR
🏦 For Banks & Fintech Companies:
a. Protects financial transactions and customer data
b. Meets regulatory mandates (RBI, PCI-DSS, SWIFT CSP)
c. Prevents fraud, account takeover, and API abuse
d. Secures mobile payment apps and banking portals
🏛 For Government Agencies:
a. Protects national infrastructure and citizen data
b. Prevents espionage and targeted attacks
c. Ensures operational continuity of critical services
📱 For Tech Companies / Startups:
a. Ensures secure development lifecycle
b. Prevents IP theft
c. Builds trust with investors and users
🌐 For Cloud-Driven Enterprises:
a. Ensures secure deployments on AWS, Azure, GCP
b. Detects IAM misconfigurations, bucket leaks, privilege escalations
4. Types of VAPT Across Different Technology Domains
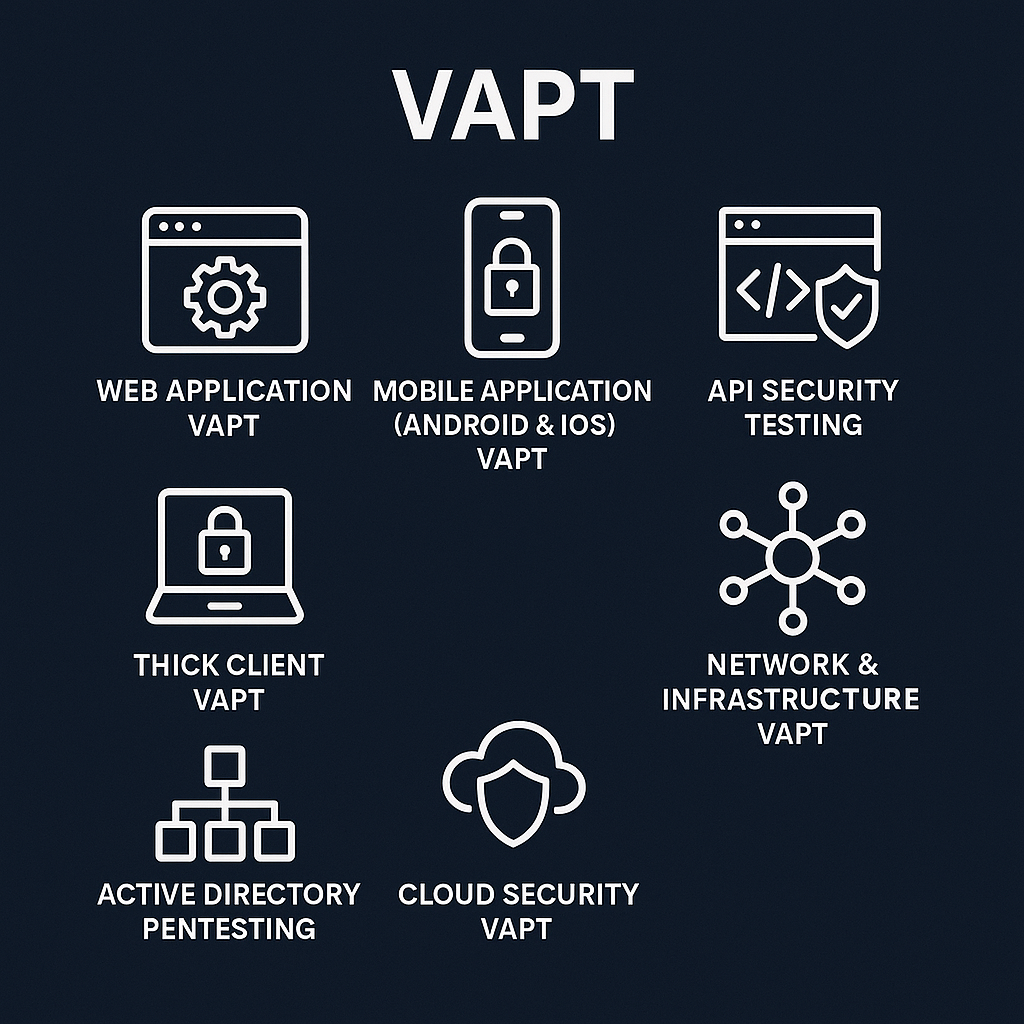
Cybersecurity is no longer a technical function — it is a business survival strategy.
As attack vectors expand across web, mobile, cloud, API, AD, and infrastructure layers, organizations must adopt regular and comprehensive VAPT programs to stay ahead of adversaries.
Whether you are a startup, bank, fintech company, government body, or a large enterprise, the question is not “Will we be attacked?”
The real question is:
“How prepared are we when the attack happens?”
VAPT ensures that the answer is always:
“We are ready.”
Leave a Reply